Model: Decision & Risk
Covers strategies for sound choices under uncertainty, including probabilistic thinking and risk mitigation techniques.

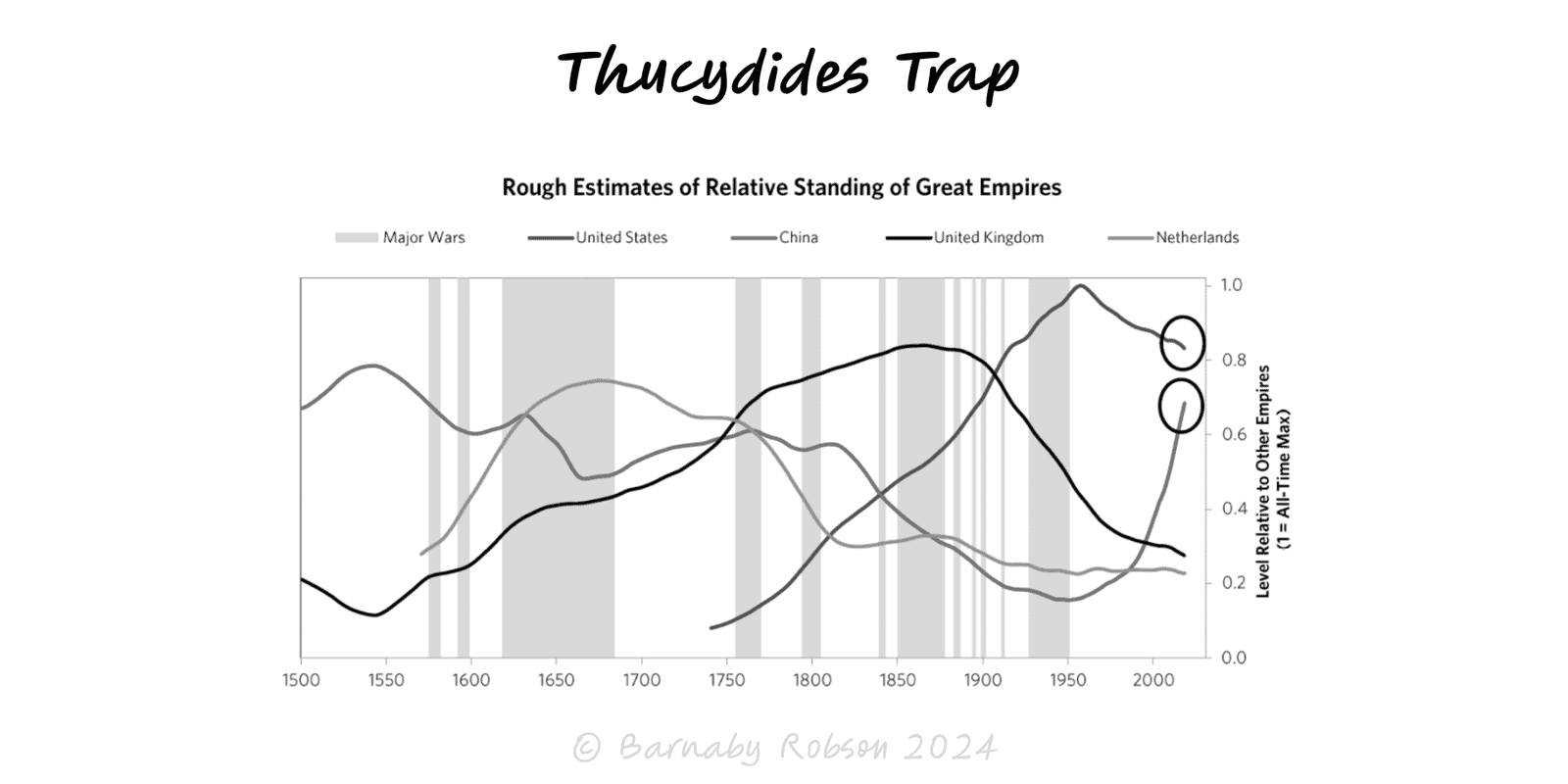
Thucydides Trap
When a rising power threatens to displace a ruling power, fear and miscalculation can tip competition into conflict unless incentives and guardrails are redesigned.
·
Barnaby

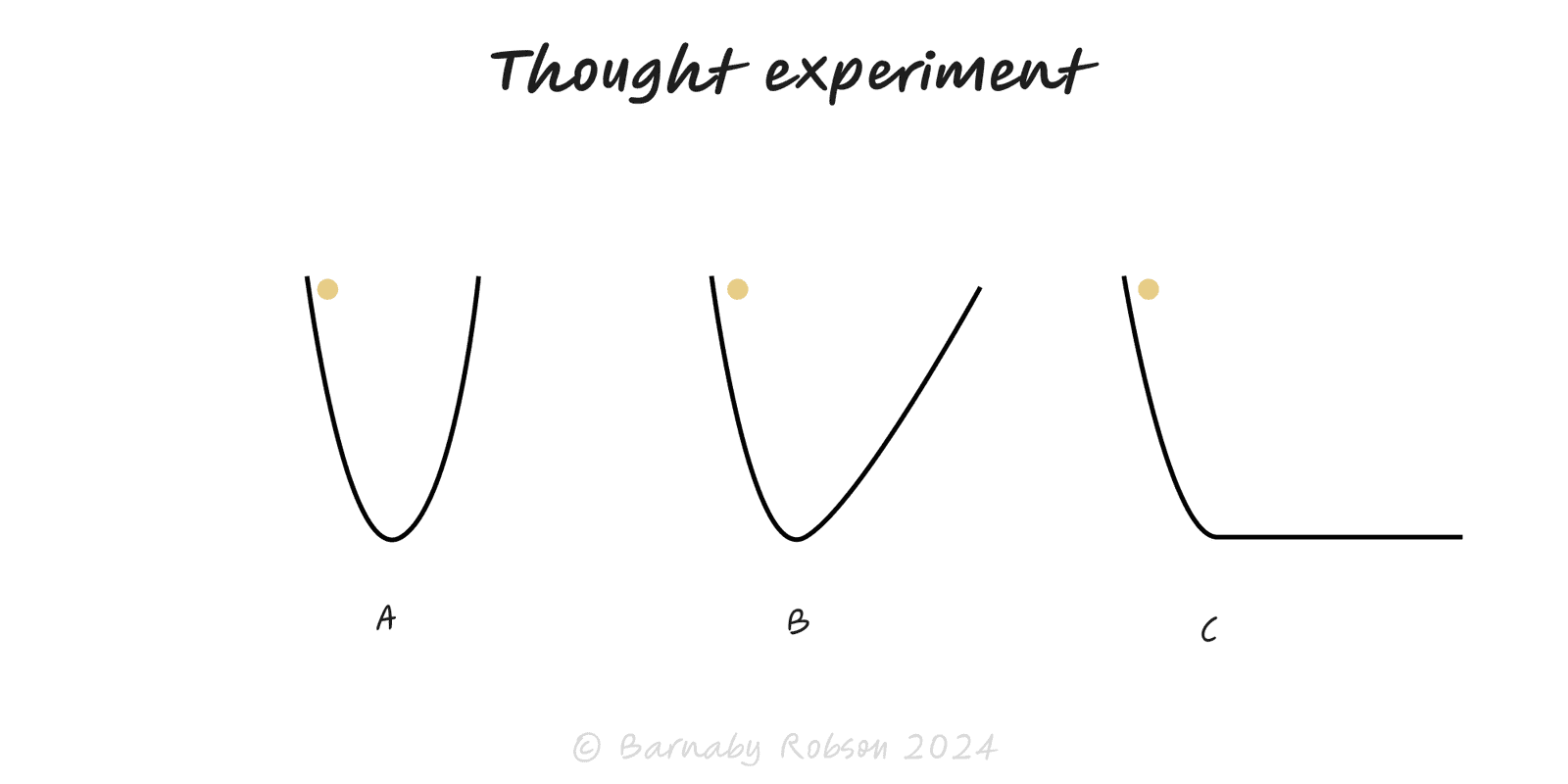
Thought Experiment
Use a carefully imagined scenario to test an idea’s logic, expose assumptions, and predict consequences—before you spend time or money.
·
Barnaby

The Map is not the Territory
All models are simplifications. Don’t confuse the representation (map, metric, plan, narrative) with the thing itself—and update the map when facts change.
·
Barnaby

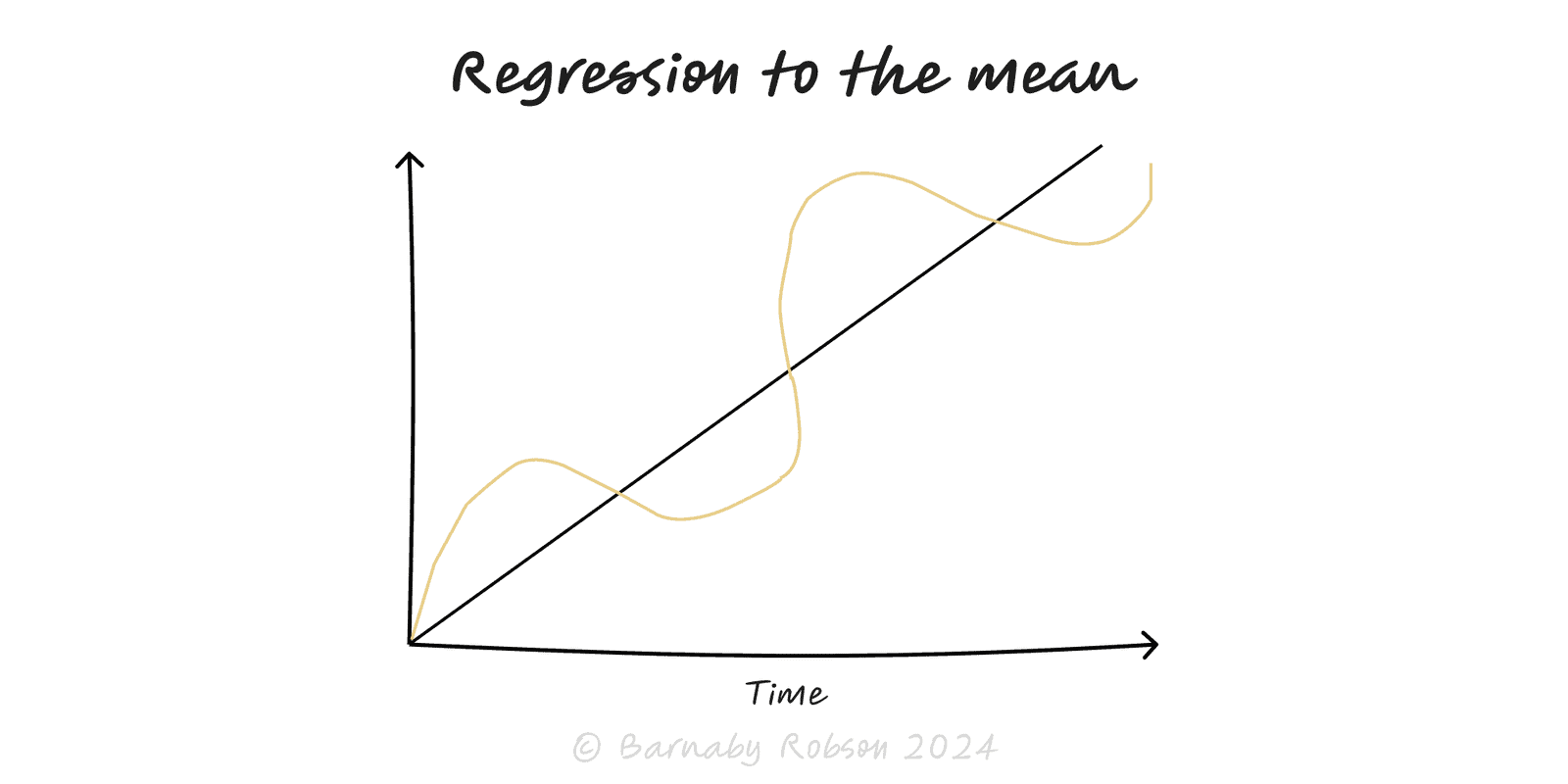
Regression to the Mean
Extreme results are usually followed by more typical ones—even without any real change.
·
Barnaby

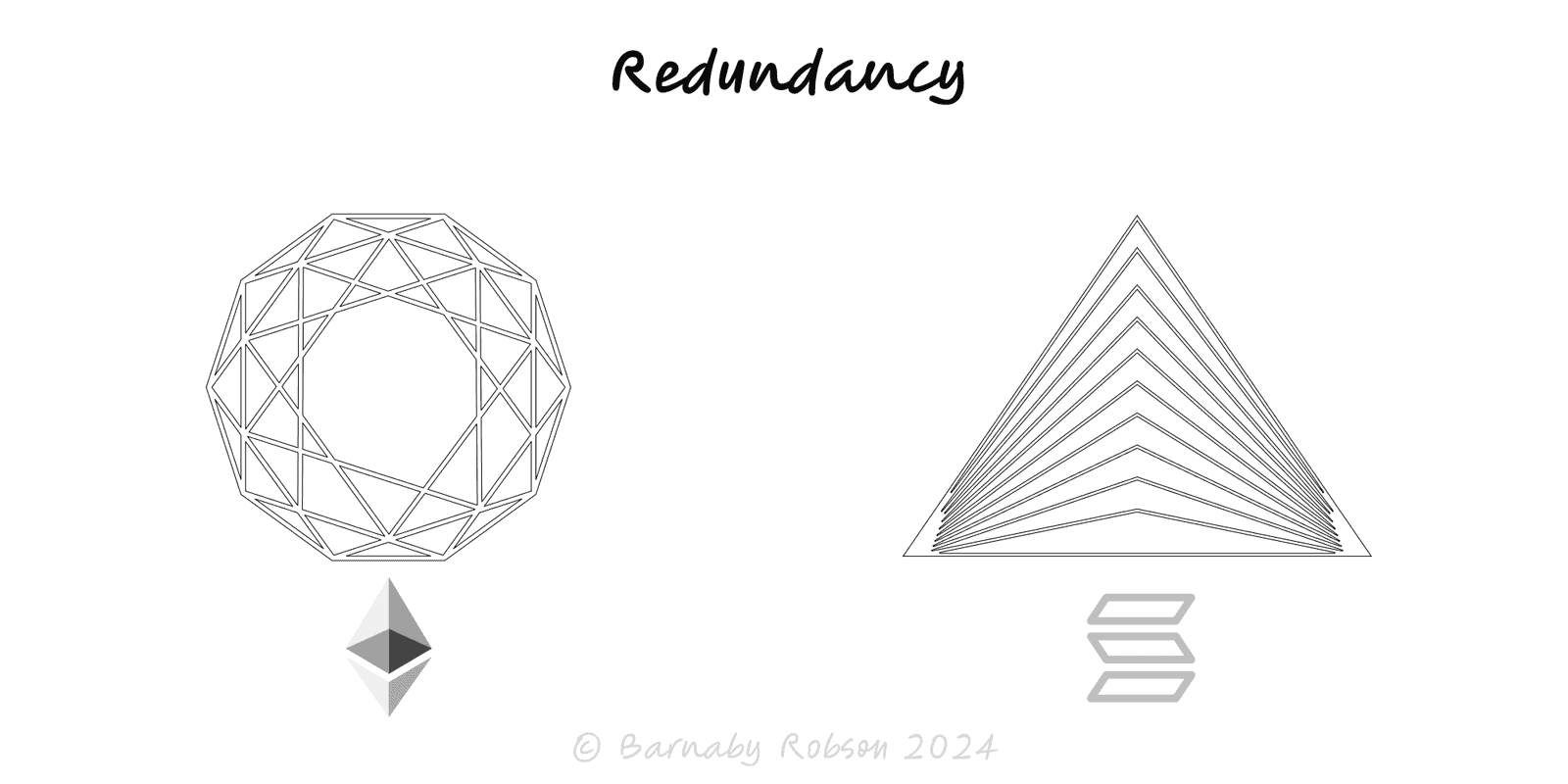
Redundancy
Add independent alternatives so one failure doesn’t stop the outcome; test failover so the backup isn’t imaginary.
·
Barnaby

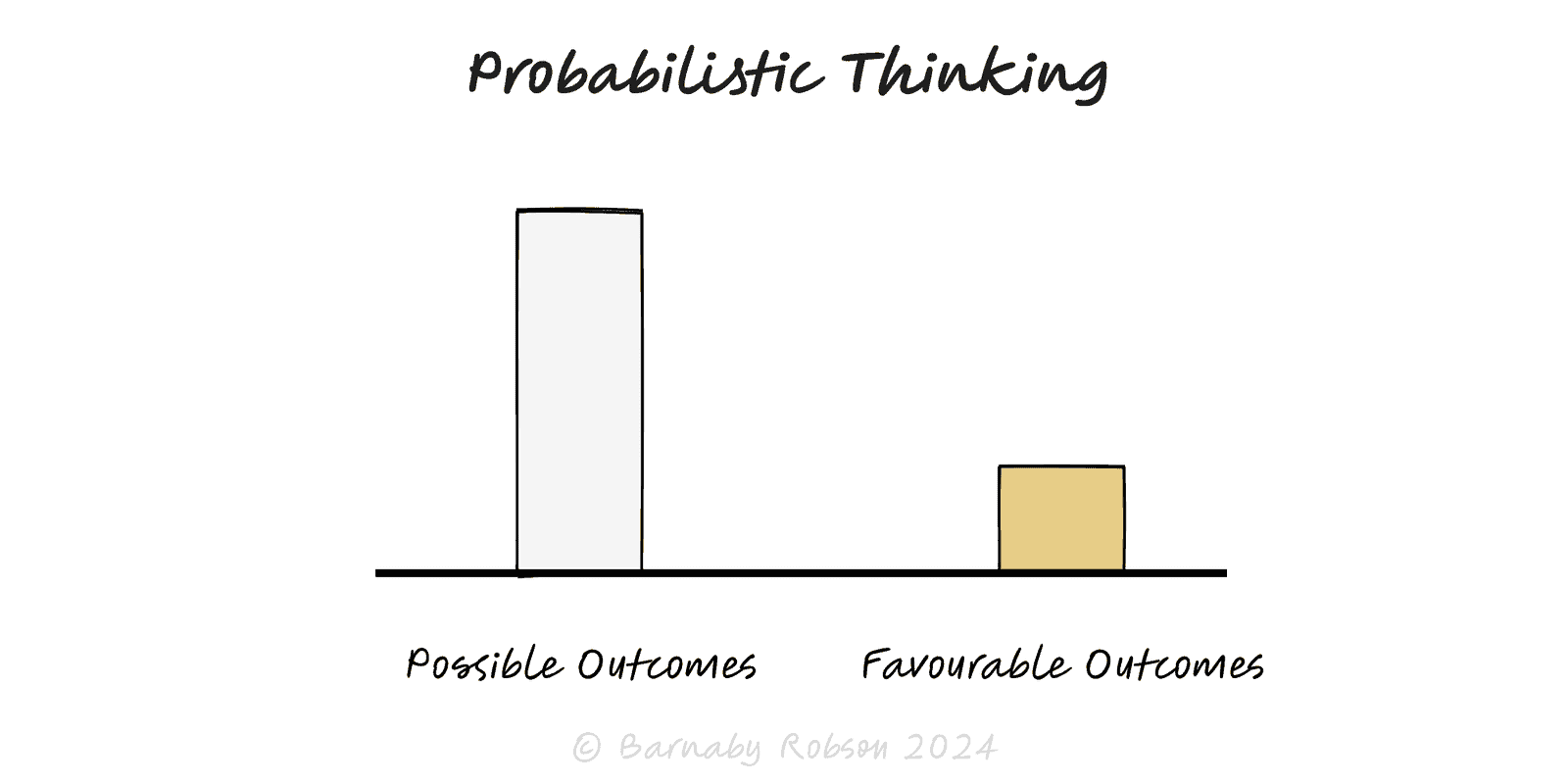
Probabilistic Thinking
Reason in degrees of belief, not certainties: use base rates, ranges, and expected value—then update as evidence arrives.
·
Barnaby


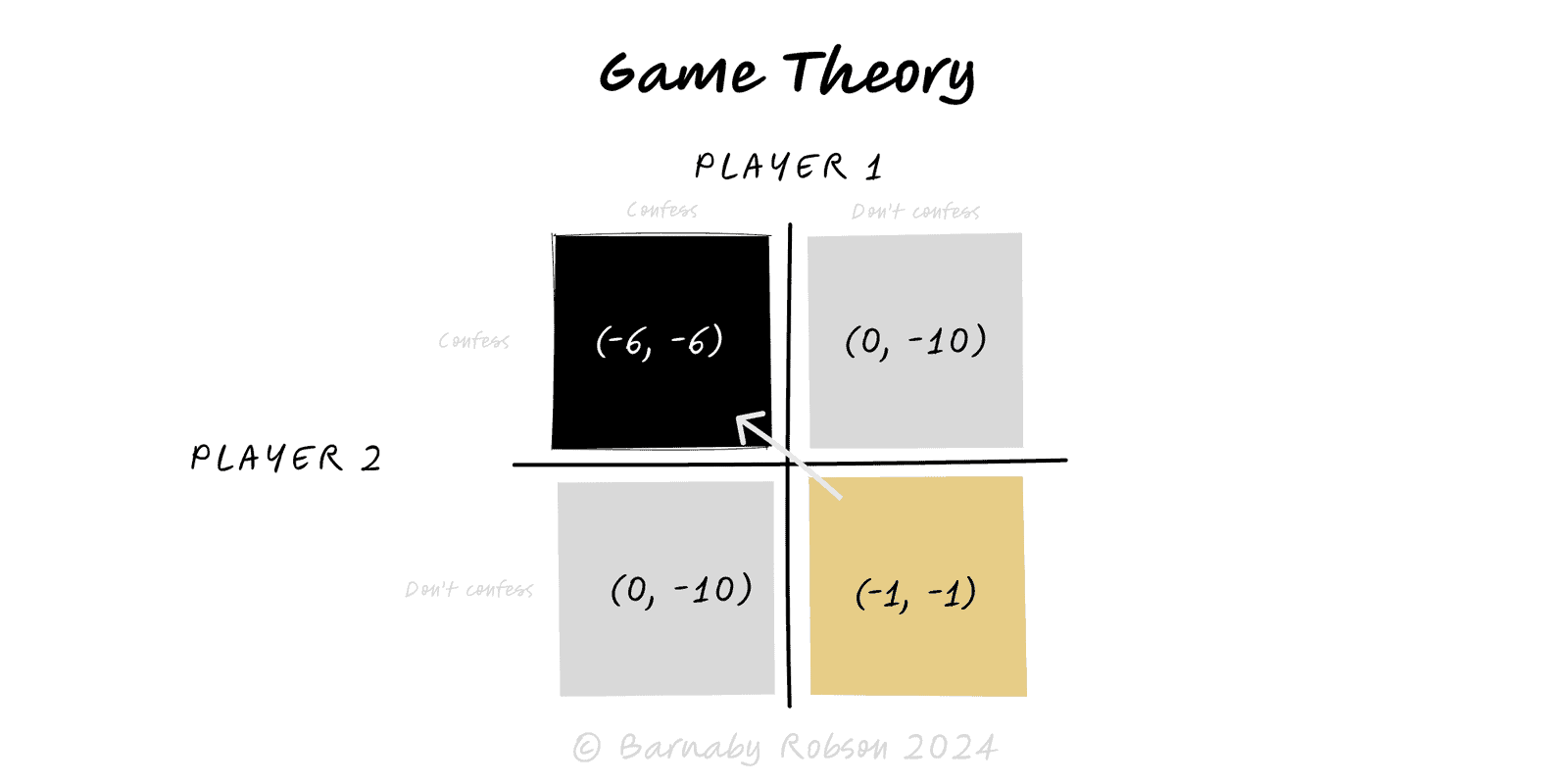
Game Theory
Model strategic situations where outcomes depend on your choice and others’ choices—then design moves or rules to shift the equilibrium.
·
Barnaby

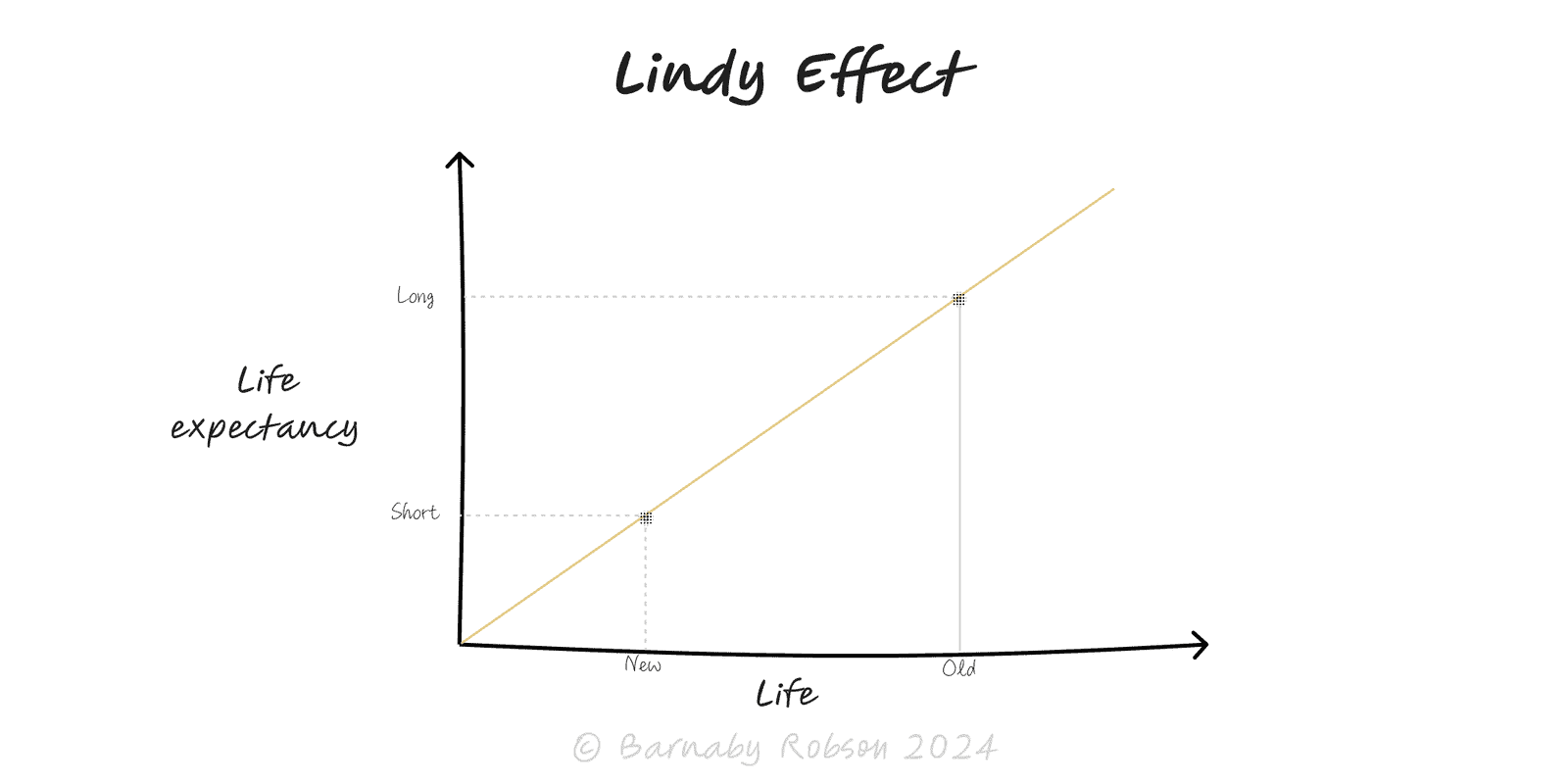
Lindy Effect
For non-perishable things (ideas, books, protocols), the older it is, the longer it’s likely to last.
·
Barnaby

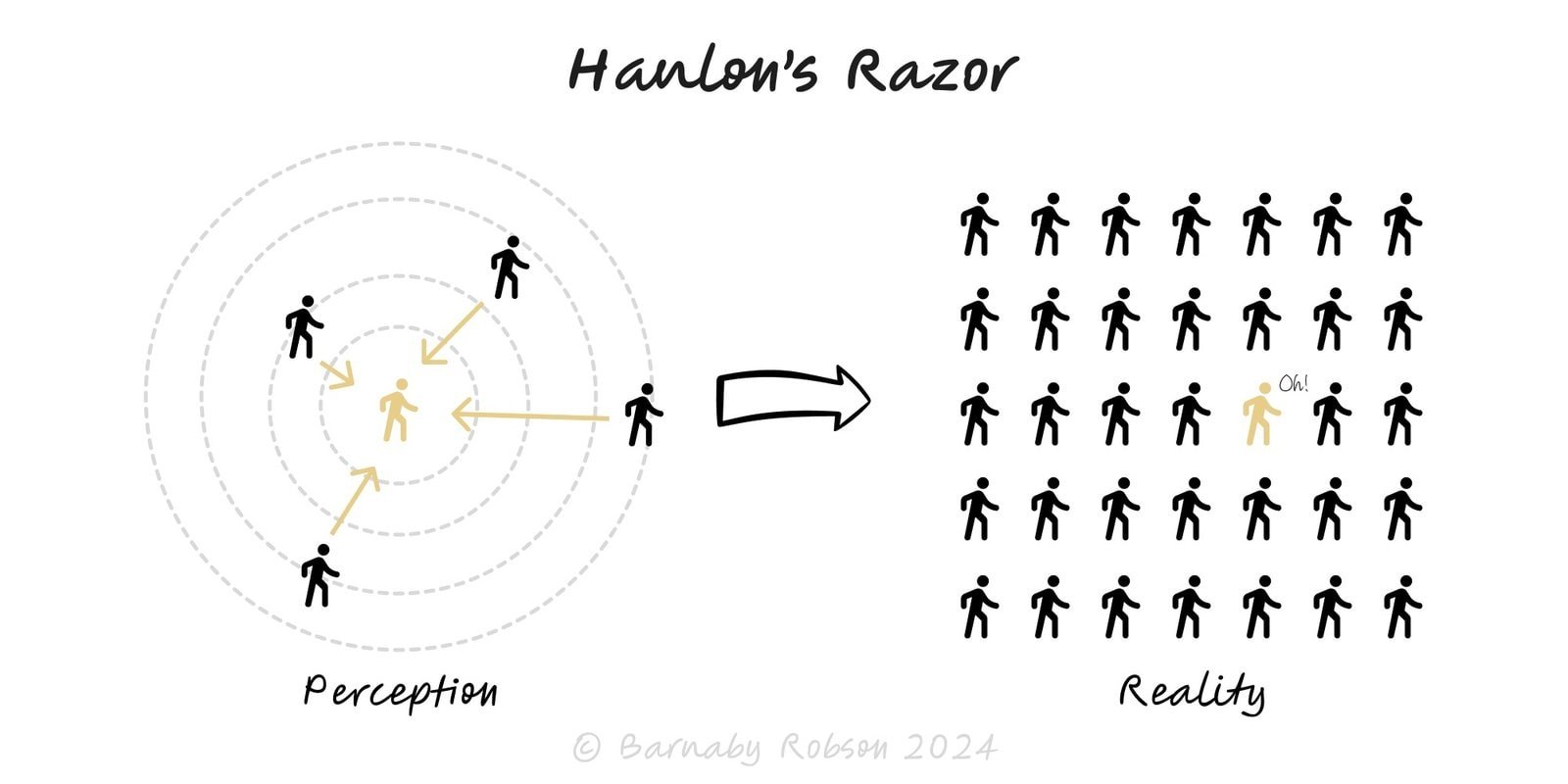
Hanlon’s Razor
Don’t attribute to malice what can be explained by error, ignorance or misaligned incentives.
·
Barnaby

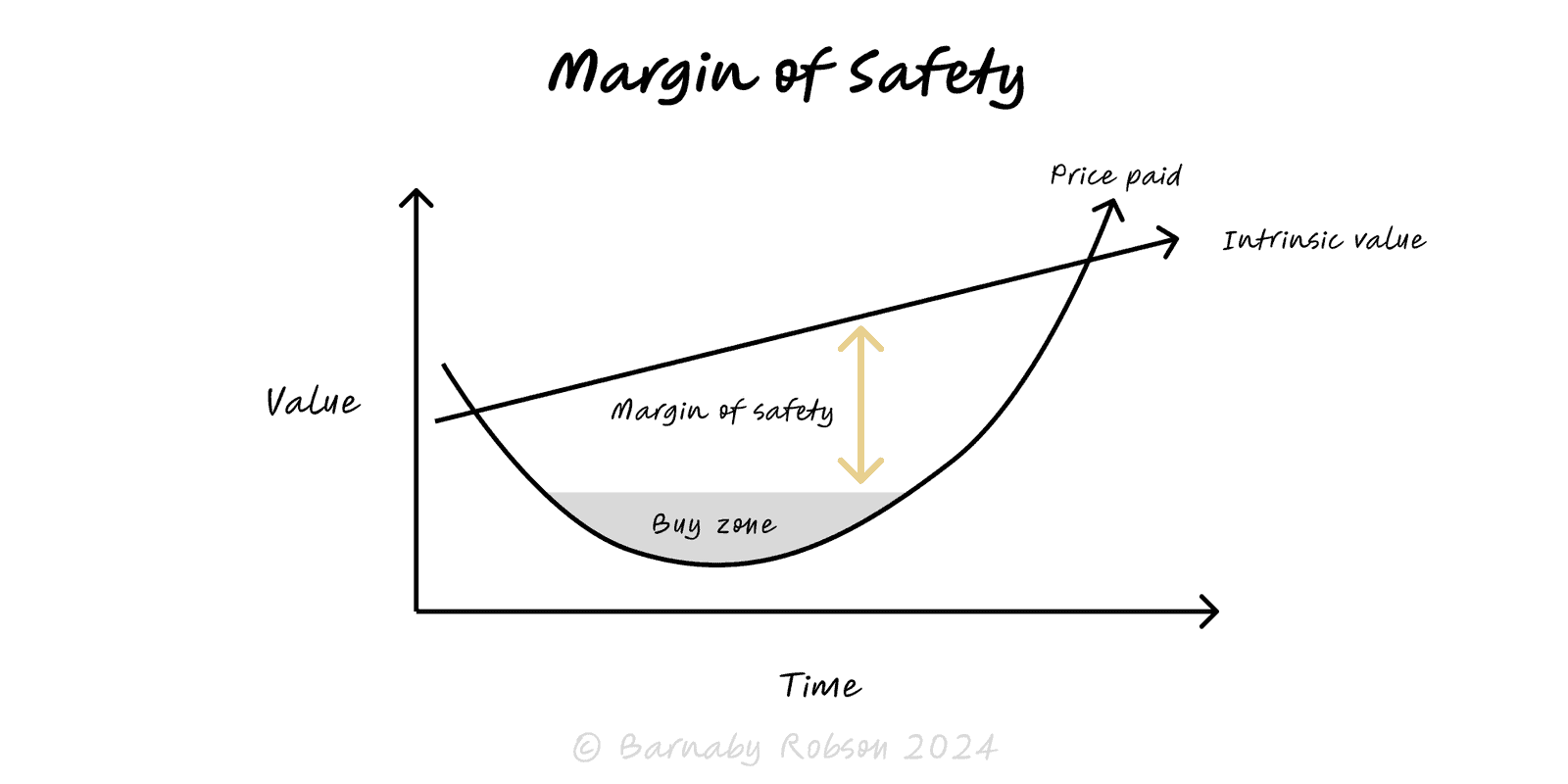
Margin of Safety
Deliberately leave room for error—buy below value, build above load, plan beyond the optimistic case—so mistakes and volatility don’t cause ruin.
·
Barnaby

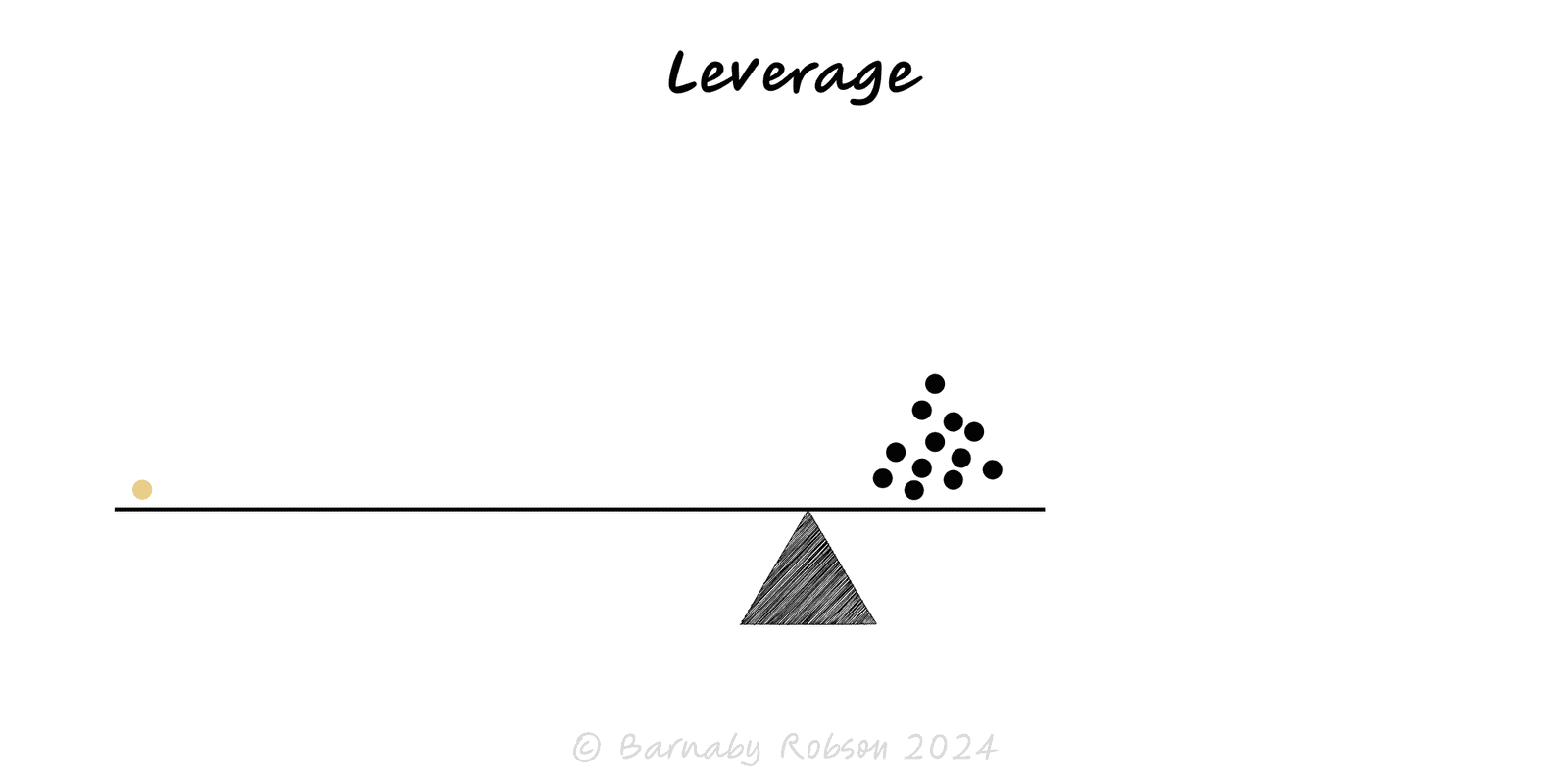
Leverage
Use small inputs to create large outputs by applying amplifiers — capital, code, media, process, partnerships. Leverage magnifies both gains and losses.
·
Barnaby