Munger’s Tendencies
Munger’s catalogue of 25 psychological tendencies that systematically distort judgement — and how to guard against them.
Author
Charlie Munger
Model type
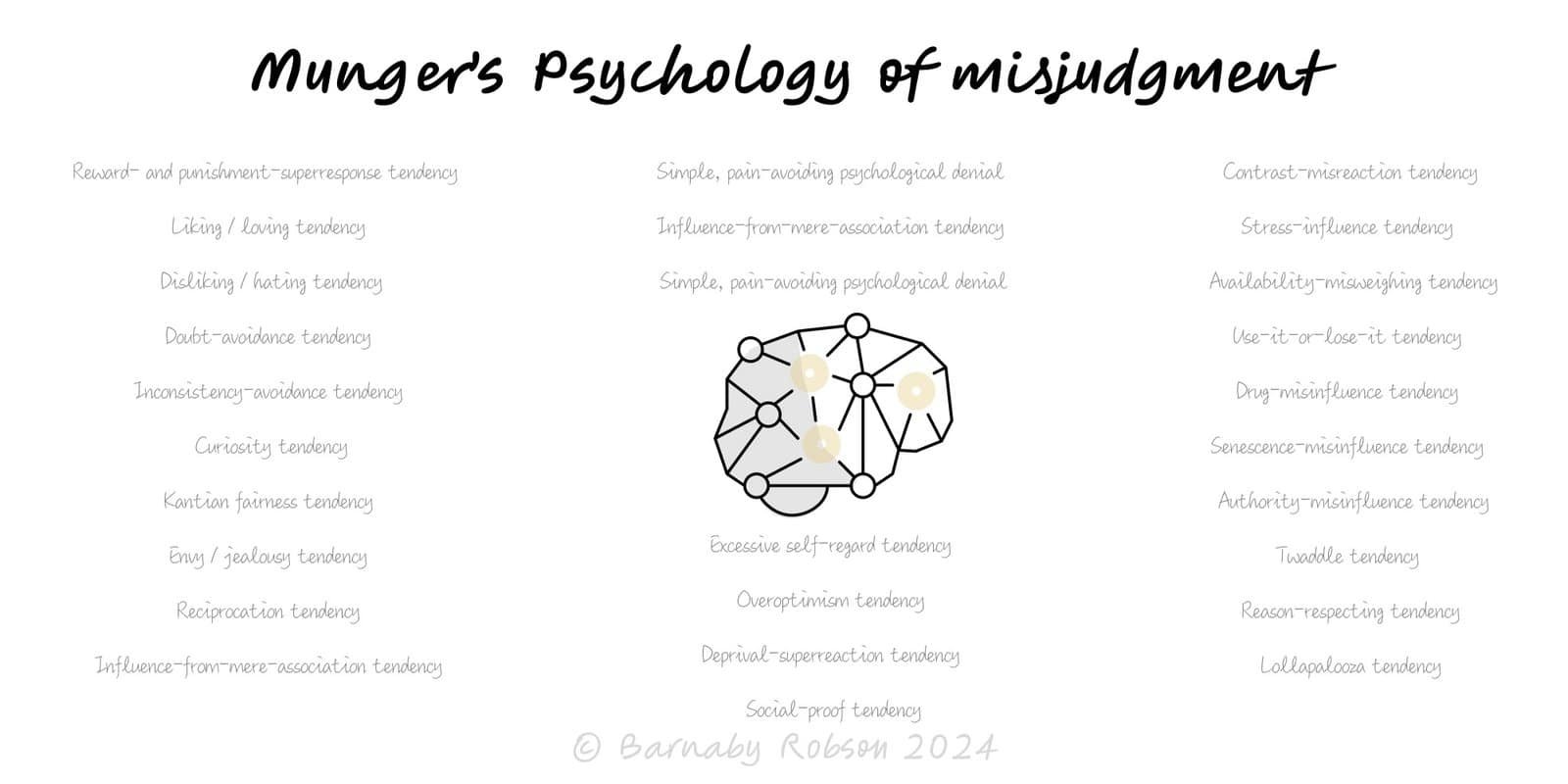
Munger’s catalogue of 25 psychological tendencies that systematically distort judgement — and how to guard against them.
Charlie Munger

Charlie Munger synthesised classic findings from psychology into a practical list for investors and operators. The core idea: incentives, social dynamics, and cognition interact; severe errors often arise when several tendencies stack into a lollapalooza effect.
Why a list, not a graphic for each? The tendencies don’t form a neat taxonomy and frequently compound. A clear list supports scanning, pre-mortems, and auditing decisions.
Reward- and punishment-superresponse – behaviour follows incentives; expect gaming.
Liking/Loving – we overrate those we like; halo effects.
Disliking/Hating – we underrate those we dislike; horn effects.
Doubt-avoidance – premature closure under uncertainty.
Inconsistency-avoidance – stick with prior commitments to look consistent.
Curiosity – tendency to seek/attend to novel information.
Kantian fairness – bias toward perceived fairness norms.
Envy/Jealousy – relative position distorts choices.
Reciprocation – urge to return favours, even when maladaptive.
Influence-from-mere-association – adjacent cues colour judgement.
Simple, pain-avoiding psychological denial – reject hard truths.
Excessive self-regard – overconfidence, self-serving attributions.
Overoptimism – base-rate neglect, planning fallacy.
Deprival-superreaction – losses loom larger than gains.
Social proof – follow the crowd, especially under ambiguity.
Contrast-misreaction – evaluations depend on nearby anchors.
Stress-influence – pressure narrows attention and impairs judgement.
Availability-misweighing – vivid/recent beats relevant/base rate.
Use-it-or-lose-it – skills and circuits atrophy without use.
Drug-misinfluence – chemistry alters preferences and risk perception.
Senescence-misinfluence – ageing changes cognition and incentives.
Authority-misinfluence – deference to perceived experts or rank.
Twaddle – love of narrative and jargon over substance.
Reason-respecting – compliance when given “reasons,” even weak ones.
Lollapalooza – multiple tendencies combine to produce extreme outcomes.
Decision pre-mortems: scan for stacked tendencies before sign-off.
Deal and board papers: include a “bias audit” sidebar with concrete mitigations.
Sales/comp design: test incentives for gaming and unintended behaviours.
Post-mortems: classify misses by dominant tendencies; update playbooks.
Define the decision and the actors at risk of bias.
Run the checklist; mark any stacking (2+ tendencies on the same choice).
Design countermeasures: base-rate tables, independent checks, incentive tests, written pre-commitments.
Record the bias audit with the decision memo; review in post-mortems.
n/a – understanding these tendencies is the cure to many cognitive pitfalls. That was Charlie Munger’s point
Click below to learn other mental models

Before building, map the space: the key forks, dead ends and dependencies—so you can choose a promising path and run smarter tests.
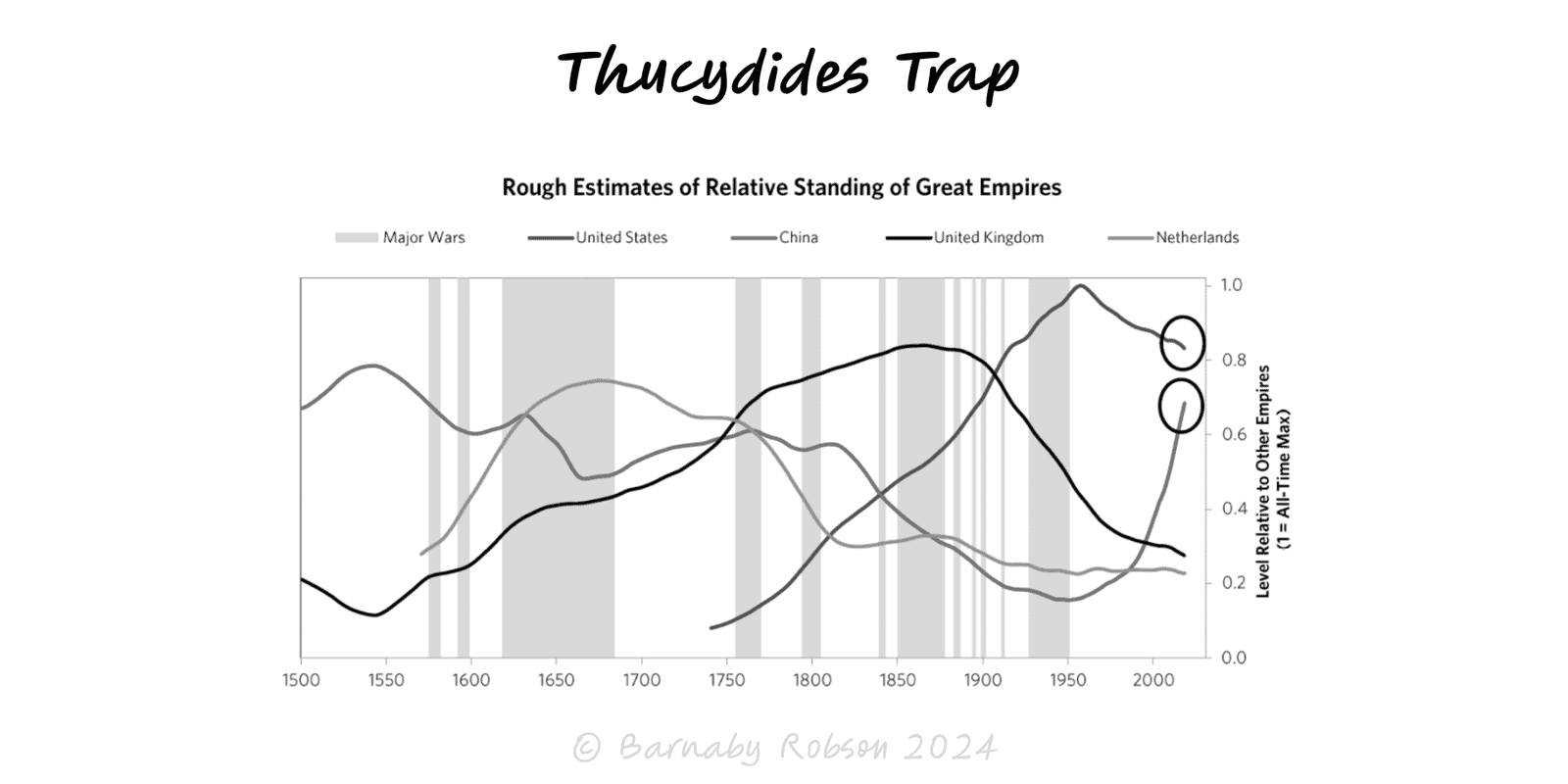
When a rising power threatens to displace a ruling power, fear and miscalculation can tip competition into conflict unless incentives and guardrails are redesigned.
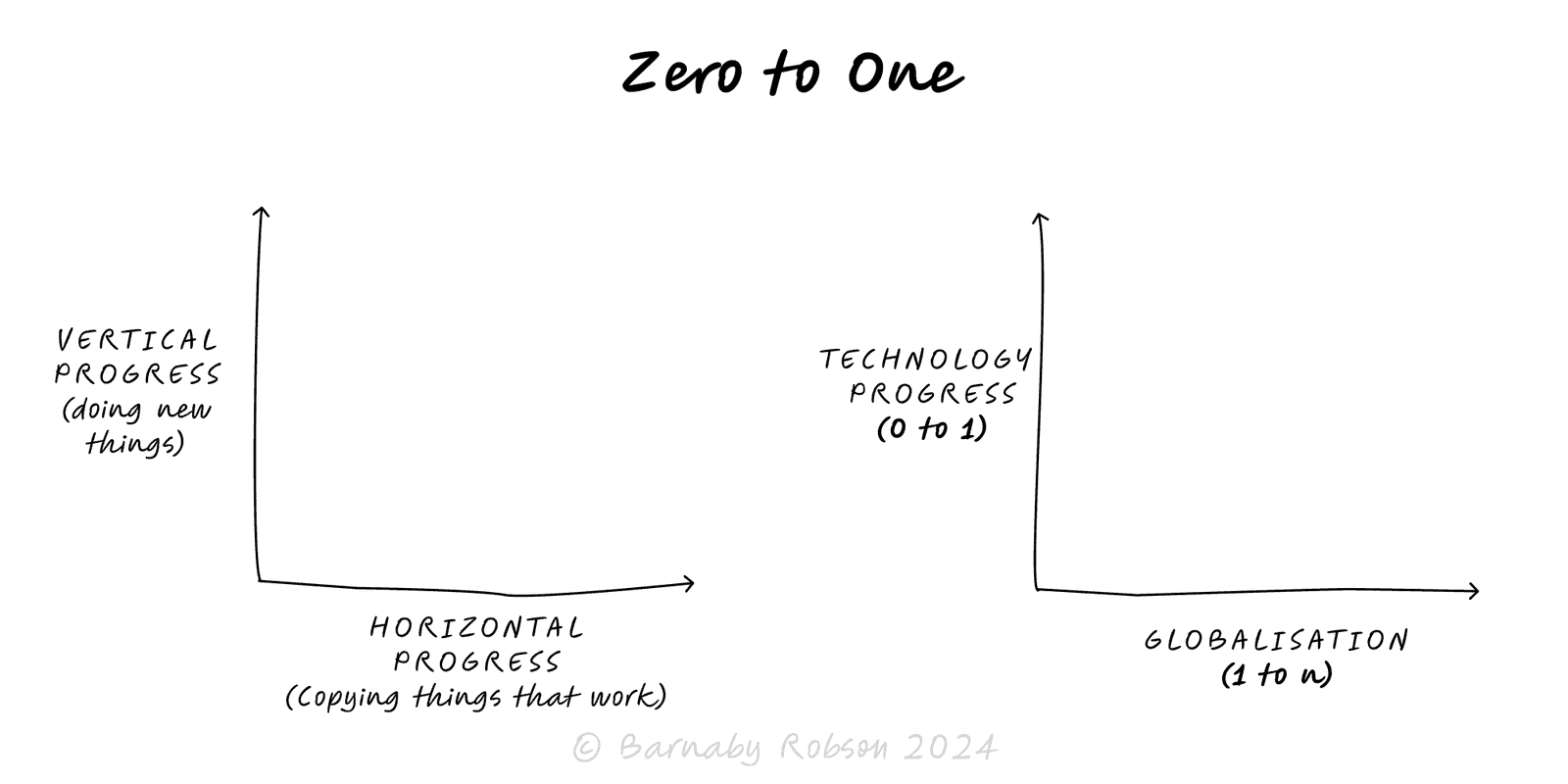
Aim for vertical progress—create something truly new (0 → 1), not just more of the same (1 → n). Win by building a monopoly on a focused niche and compounding from there.