Multiplying by Zero
A single failure mode can zero the outcome (eg, safety, compliance).
Author
General usage (probability, reliability engineering, decision theory)
Model type
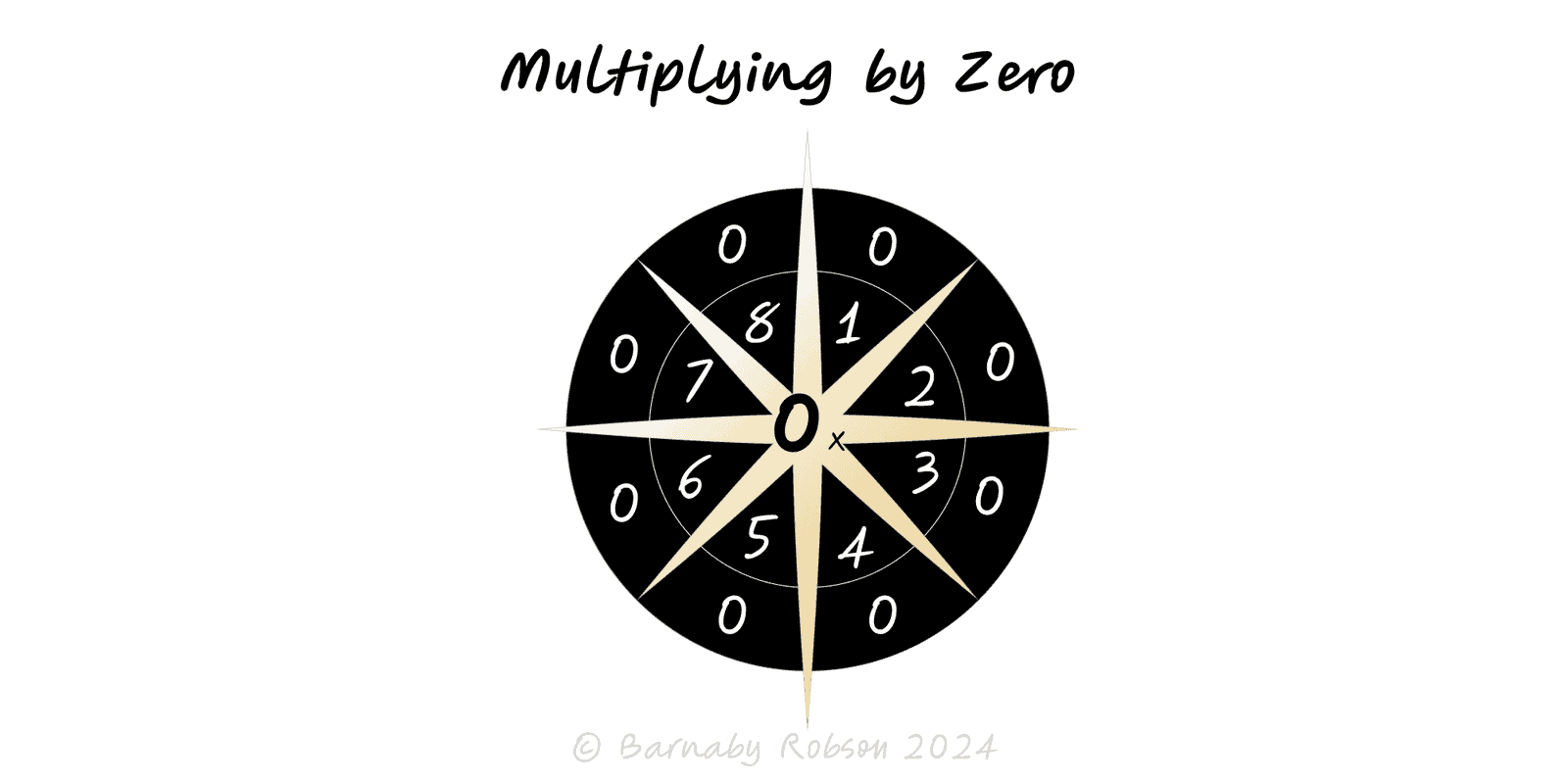
A single failure mode can zero the outcome (eg, safety, compliance).
General usage (probability, reliability engineering, decision theory)

Some outcomes are the product of several factors: reliability across components, conversions across a funnel, steps in a process, survival across risks. If any factor drops to 0 (component down, step blocked, licence expired, cash = 0), the overall result collapses. Unlike additive trade-offs, deficiencies here are non-compensatory: excellence in one area can’t cancel a zero elsewhere.
Product rule – Overall result ≈ f₁ × f₂ × … × fₙ. If any fᵢ = 0, the product is 0.
Series reliability – System uptime = Π(availabilityᵢ). A single SPOF with 0% availability takes uptime to 0.
Funnel math – Total conversion = Π(stage conversionᵢ). A broken stage (0%) kills the funnel.
Geometric mean logic – Long-run performance tends to the geometric mean; ruin events (wealth → 0, trust → 0) dominate.
AND vs OR – If success requires all steps (AND), guard against zeros; if any will do (OR), add alternatives to avoid zeros.
Ops & reliability – remove single points of failure; N+1 servers, second suppliers, offline modes.
Finance & risk – avoid ruin; cap position sizes, diversify uncorrelated risks, keep cash buffers.
Growth & product – fix the lowest funnel step first; ensure a non-zero “first value” rate.
Compliance & safety – one lapse can zero the licence or trust; design three-layer controls.
Supply chain – dual-source critical parts; safety stock on bottlenecks.
People & teams – minimum bars on ethics, security, and handoffs; one failure zeros outcomes.
Map the series – list the factors that must all succeed (components, stages, approvals, suppliers).
Find zeros and near-zeros – where can availability, quality or conversion hit 0% (or effectively 0%)?
Set floors – define non-negotiable minimums per factor (e.g., availability ≥ 99.5%, first-value ≥ 30%).
Add OR paths – redundancy, alternates, retries, cached results, second suppliers, manual fallback.
Protect against ruin – limit leverage, ring-fence experiments, enforce kill switches and circuit breakers.
Instrument early warnings – alarms on floor breaches; track the worst stage, not just the average.
Fix in order of constraint – improve the smallest factor first; re-compute the product after each fix.
Rehearse failure – game days, chaos tests, supplier drills; ensure fallbacks actually work.
Linear thinking – treating multiplicative chains as additive; “over-investing” elsewhere can’t offset a zero.
Hidden correlation – redundant paths that fail together (same region, vendor, library).
Over-buffering – redundancy everywhere raises cost/complexity; protect SPOFs and one-way doors first.
Complacent averages – great mean performance hides a few zero days; watch percentiles and minima.
Ethics/trust zeros – a single breach can zero reputation; prevention beats apology.
Click below to learn other mental models

Before building, map the space: the key forks, dead ends and dependencies—so you can choose a promising path and run smarter tests.
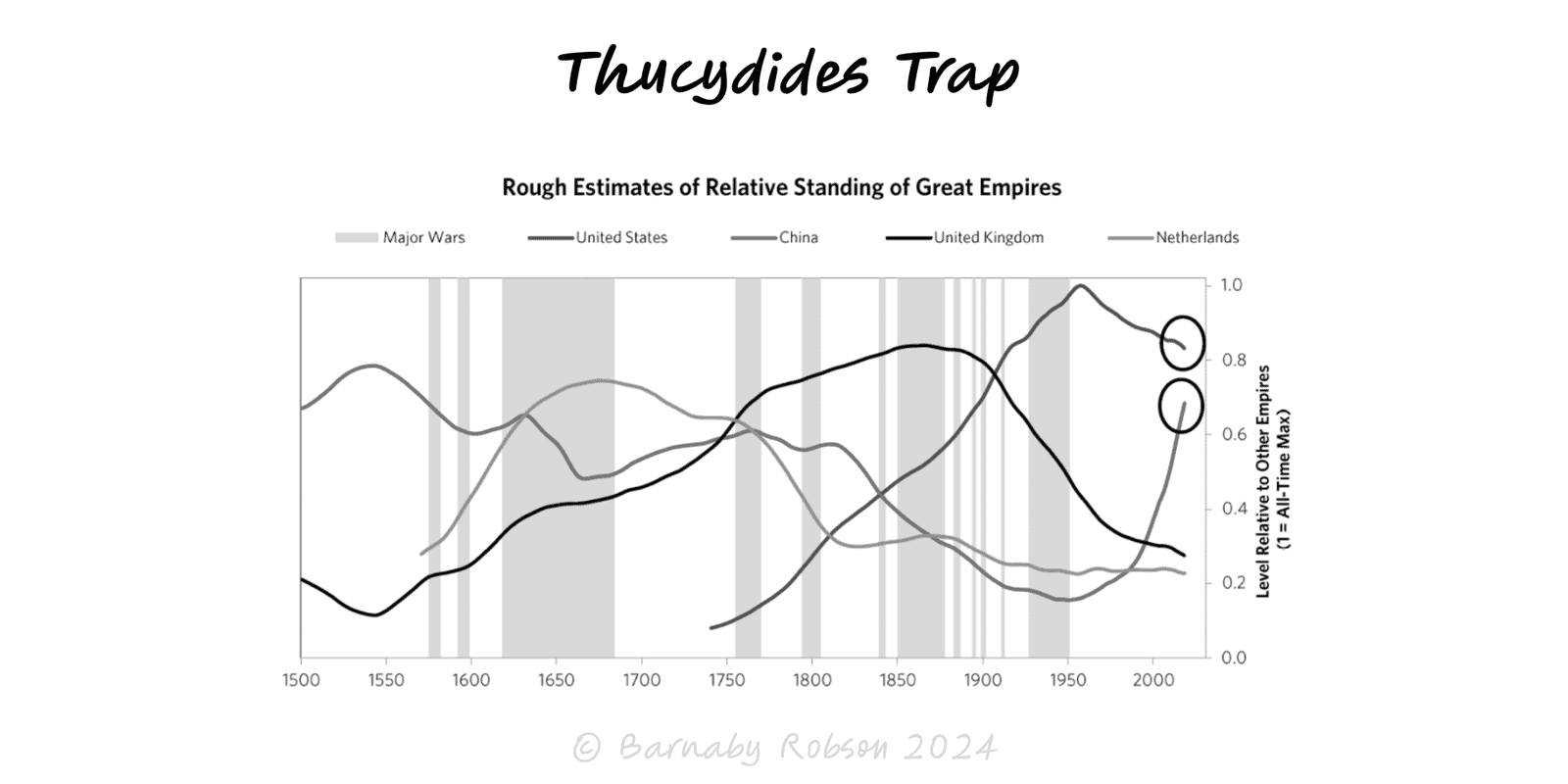
When a rising power threatens to displace a ruling power, fear and miscalculation can tip competition into conflict unless incentives and guardrails are redesigned.
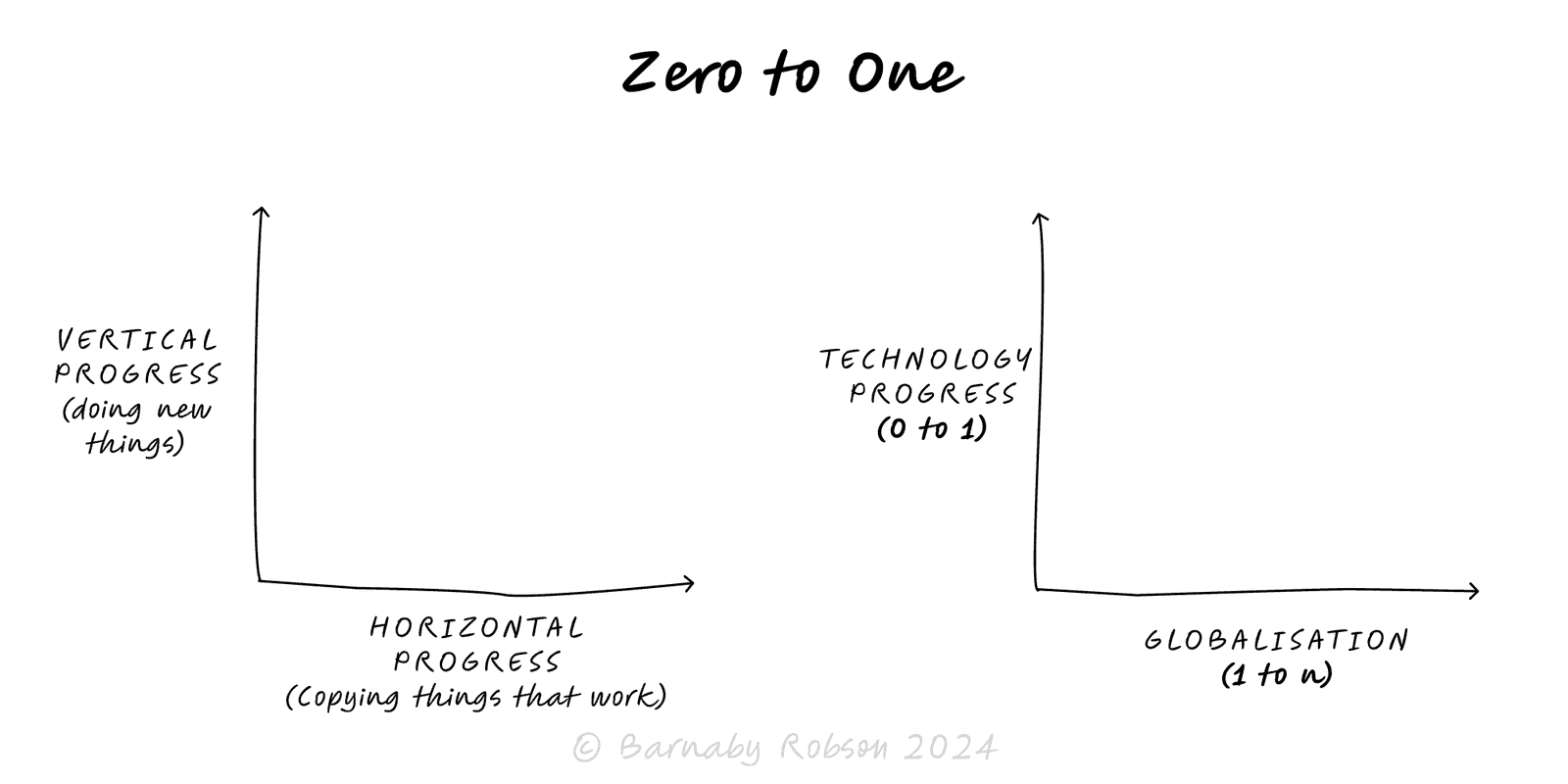
Aim for vertical progress—create something truly new (0 → 1), not just more of the same (1 → n). Win by building a monopoly on a focused niche and compounding from there.